I'm a paragraph. Click here to add your own text and edit me. It's easy.
I'm a paragraph. Click here to add your own text and edit me. It's easy.
TRANSCENDENT FOURTH TESLA
http://vator.tv/news/2017-04-03-are-the-big-three-automakers-now-the-big-four
Are the Big Three automakers now the Big Four?
After a record setting quarter, Tesla is now a more valuable company than Ford
For a long time we've had what have been known as the Big Three American automobile makers, all based in Detriot: Ford, General Motors and Chrysler. Now it may finally be time to add a new member to that club, one with no connections to the Motor City.
On Monday, Tesla announced that delivered over 25,000 vehicles in the first quarter of 2017, a new record, and a 69 percent increase over the same quarter in 2016. Analysts has been estimating deliveries to be closer to 23,000.
Read more at http://vator.tv/news/2017-04-03-are-the-big-three-automakers-now-the-big-four#pkuPVXsD8KPYQzQt.99
Read more at http://vator.tv/news/2017-04-03-are-the-big-three-automakers-now-the-big-four#pkuPVXsD8KPYQzQt.99

ODYSSEUS AND THE MAST TIED TO THE CRUCIFIXION
Quadrant
Four Times of the Day is a series of four paintings by English artist William Hogarth. Completed in 1736, they were reproduced as a series of four engravings published in 1738. They are humorous depictions of life in the streets of London, the vagaries of fashion, and the interactions between the rich and poor. Unlike many of Hogarth's other series, such as A Harlot's Progress, A Rake's Progress, Industry and Idleness, and The Four Stages of Cruelty, it does not depict the story of an individual, but instead focuses on the society of the city. Hogarth intended the series to be humorous rather than instructional; the pictures do not offer a judgment on whether the rich or poor are more deserving of the viewer's sympathies: while the upper and middle classes tend to provide the focus for each scene, there are fewer of the moral comparisons seen in some of his other works.
The four pictures depict scenes of daily life in various locations in London as the day progresses. Morningshows a prudish spinster making her way to church in Covent Garden past the revellers of the previous night; Noon shows two cultures on opposite sides of the street in St Giles; Evening depicts a dyer's family returning hot and bothered from a trip to Sadler's Wells; and Night shows disreputable goings-on around a drunken freemason staggering home near Charing Cross.

The Four Stages of Cruelty is a series of four printed engravings published by English artist William Hogarth in 1751. Each print depicts a different stage in the life of the fictional Tom Nero.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Four_Stages_of_Cruelty
In common with other prints by Hogarth, such as Beer Street and Gin Lane, The Four Stages of Cruelty was issued as a warning against immoral behaviour, showing the easy path from childish thug to convicted criminal. His aim was to correct "that barbarous treatment of animals, the very sight of which renders the streets of our metropolis so distressing to every feeling mind".[1] Hogarth loved animals, picturing himself with his pug in a self-portrait, and marking the graves of his dogs and birds at his home in Chiswick.[2]
In the second plate, the scene is Thavies Inn Gate (sometimes ironically written as Thieves Inn Gate), one of the Inns of Chancery which housed associations of lawyers in London.[12] Tom Nero has grown up and become a hackney coachman, and the recreational cruelty of the schoolboy has turned into the professional cruelty of a man at work. Tom's horse, worn out from years of mistreatment and overloading, has collapsed, breaking its leg and upsetting the carriage. Disregarding the animal's pain, Tom has beaten it so furiously that he has put its eye out. In a satirical aside, Hogarth shows four corpulent barristers struggling to climb out of the carriage in a ludicrous state. They are probably caricatures of eminent jurists, but Hogarth did not reveal the subjects' names, and they have not been identified. Elsewhere in the scene, other acts of cruelty against animals take place: a drover beats a lamb to death, an ass is driven on by force despite being overloaded, and an enraged bull tosses one of its tormentors

Second stage of cruelty (Plate II)
THE CRUCIFIX IN A RAKES PROGRESS BY HOGARTH- IN THE FINAL PAINTING BY HOGARTH THERE IS AN INSANE MAN IN THE BACKGROUND AND HE IS PRAYING TO A LARGE CRUCIFIX OF JESUS
PLATE V
http://www.darvillsrareprints.com/Hogarth%20Rake%27s%20Progress.htm
http://www.darvillsrareprints.com/images/Hogarth/Rake's%20Progress%202015/Rakes-Progress-plate-8.jpg
The rake, a stately, attractive figure, is in the act of prostituting himself in much the same way as the harlot did in Plate II. As he slips the ring on his wife's finger, he glances calculatingly at her young maid. At the feet of these richly dressed figures, a ragged urchin with his toes peeping through his righ shoe positions a kneeler for the bride. The wife, and overdressed, one-eyed, hunchbacked creature, leers and seems to wink at the clergyman, a figure much more her match in age and looks. The small crucifix on her breast and the halo-like "IHS" above her head cast her satirically as a saint. A large, aggressive dog and a smaller one-eyed bitch mirror the alliance taking place at the right. In the background a churchwarden battles with Sarah Young and her clawing mother, who have come with the rake's child to prevent the marriage.
PLATE VIII
In the hospital science has claimed two victims. The fellow peering at the ceiling through a roll of paper which he imagines to be a telescope is an astronomer. Behind him the fellow who has drawn the ship, mortar and shot, earth, moon and various geometric patterns is attempting to discover a scheme for calculating longitude. Religion has two adherents here. The man in the first cell sitting on straw chained to a rock is a fanatic; he keeps a crucifix and icons of three saints ("St. Lawrance, St. Athanatius [C]lemen[t]") beside him. His body is contorted in prayer and his adoring face is screwed up into the likeness of a wild animal. The person on the stairs with the cone-shaped hat and triple cross who seems to sing imagines himself the pope.

FOUR TYPES
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Social_evolution
Social evolution is a subdiscipline of evolutionary biology that is concerned with social behaviors that have fitness consequences for individuals other than the actor. Social behaviors can be categorized according to the fitness consequences they entail for the actor and recipient.
-
Mutually beneficial – a behavior that increases the direct fitness of both the actor and the recipient
-
Selfish – a behavior that increases the direct fitness of the actor, but the recipient suffers a loss
-
Altruistic – a behavior that increases the direct fitness of the recipient, but the actor may suffer a loss
-
Spiteful – a behavior that decreases the direct fitness of both the actor and the recipient
-

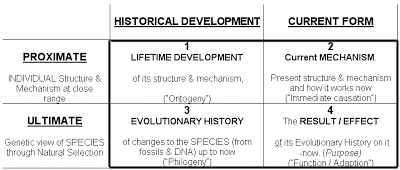
TINBERGENS FOUR QUESTIONS WAS PRETTY MUCH THE ONLY THING TAUGHT IN MY PSYCHOLOGY OF ANIMAL BEHAVIOR AT UCSD- EVERY TEST WAS BASICALLY GOING OVER THE FOUR QUESTIONS FOR DIFFERENT SPECIES
Tinbergen (1907-88) was a Dutch ethologist*[1] at Oxford after the WW2.
He delineated the four questions*[2]—or categories of explanations—of animal behavior (human), similar to Aristotle's*[3] four types of causes. This schema constitutes a basic framework of the overlapping behavioural fields of ethology, behavioural ecology, sociobiology, evolutionary psychology, and comparative psychology.
. . . CLICK ON DIAGRAM TO ENLARGE IT
This tool helps to us to maintain AWARENESS that it is a particular aspect that we are focussing on when we study any animal (human) behaviour; we must be also aware of the other 3 aspects.
Proximate Questions about the individual animal (micro view*[4])
1. LIFETIME DEVELOPMENT - how does the behaviour change with the individual's age? What early experiences are necessary for the behaviour to be shown? Which developmental steps and environmental factors play a role?
2. Current MECHANISM - what are the stimuli that elicit the present response? How has it been modified by recent learning? How do behaviour and psyche "function" on the molecular, physiological, neuro, cognitive and social level? How do these relate to each other as a structure?
Ultimate Questions about the species (macro view)
3. EVOLUTIONARY HISTORY - how does the behaviour of this species compare with similar behaviour in related species? How might it have arisen through the process of evolution? Why did the behaviour evolve in this manner and not otherwise?
4. RESULT / EFFECT - how does the behaviour affect the animal's chances of survival and reproduction? What is the function or purpose*[5] of the behaviour in this context?
BRAHMA SUTRAS FOUR CHAPTERS EACH WITH FOUR DIVISIONS IS A 16 SQUARE QUADRANT MODEL
The Brahma Sūtras consist of 555 aphorisms or sūtras, in four chapters (adhyāya), with each chapter divided into four parts (pāda).[4] Each part is further subdivided into sections called Adhikaraņas with sutras.[4] Some scholars, such as Francis Clooney, call the Adhikaraņas as "case studies" with a defined hermeneutic process.[25][26]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:DC_satellite_image.jpg
Washington, D.C., is administratively divided into four geographical quadrants of unequal size, each delineated by their ordinal directions from the medallion located in the Crypt under the Rotunda of the Capitol. Street and number addressing, centered on the Capitol, radiates out into each of the quadrants, producing a number of intersections of identically named cross-streets in each quadrant.
THE MOST POPULAR CATEGORIZATION OF KINGDOMS OF EUKARYOTS IS THE FOUR KINGDOMS THE FOURTH PROTISTS ARE TRANSCENDENT AND CONTAIN THE PREVIOUS THREE THERE ARE "PLANT LIKE ANIMAL LIKE AND FUNGI LIKE PROTISTS"
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protist
The formal taxonomic category Protoctista was first proposed in the early 1860s by John Hogg, who argued that the protists should include what he saw as primitive unicellular forms of both plants and animals. He defined the Protoctista as a "fourth kingdom of nature", in addition to the then-traditional kingdoms of plants, animals and minerals.[17] The kingdom of minerals was later removed from taxonomy in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel, leaving plants, animals, and the protists (Protista), defined as a “kingdom of primitive forms”.[18]
In 1938, Herbert Copeland resurrected Hogg's label, arguing that Haeckel's term Protista included anucleated microbes such as bacteria, which the term "Protoctista" (literally meaning "first established beings") did not. In contrast, Copeland's term included nucleated eukaryotes such as diatoms, green algae and fungi.


FOUR KINGDOM CLASSIFICATION
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Protist
In the original 4-kingdom model proposed in 1959, Protista included all unicellular microorganisms such as bacteria. Herbert Copeland proposed separate kingdoms – Mychota – for prokaryotes and – Protoctista – for eukaryotes (including fungi) that were neither plants nor animals. Copeland's distinction between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells was eventually critical in Whittaker proposing a final five-kingdom system, even though he resisted it for over a decade.[4][5]
Since ancient times, living beings were classified as either plants or animals and Linnaeus retained this system in his great work Systema Naturae in the 18thcentury, where he divided nature in three kingdoms: Regnum Animale (animal kingdom), Regnum Vegetabile (plant kingdom) and Regnum Lapideum (mineral kingdom). This system was not intended to reflect natural relationships among living organisms, since Linnaeus was a Christian and believed that all life forms were created separately by God himself just as they are today, but was created to make the study of living beings easier.
When the first unicellular organisms were discovered by Antoine van Leeuwenhoek in 1674, they were placed in one of the two kingdoms of living beings, according to their characteristics. It remained so until until 1866, when Ernst Haeckel proposed a third kingdom of life, which he called Protista, and included all unicellular organisms in it.
ORIGINALLY THERE WERE THREE KINGDOMS THEN THE TRANSCENDENT FOURTH PROTISTS WAS PROPOSD THE THREE FOUR DYNAMIC- NOTICE HOW WHITTAKRS MODEL IS A THREE PLUS ONE WHERE HE HAS ANIMAL PLANT PROTIST AND THEN SEPARATED MONERA- AS I SAID THERE ARE OTHER MODELS OF EUKARYOTES SAYING THERE ARE MORE BUT THE FOUR KINGDOM MODEL IS THE MOST POPULAR AMONG SCIENTISTS
https://earthlingnature.files.wordpress.com/2011/12/clado3.png
Since ancient times, living beings were classified as either plants or animals and Linnaeus retained this system in his great work Systema Naturae in the 18thcentury, where he divided nature in three kingdoms: Regnum Animale (animal kingdom), Regnum Vegetabile (plant kingdom) and Regnum Lapideum (mineral kingdom). This system was not intended to reflect natural relationships among living organisms, since Linnaeus was a Christian and believed that all life forms were created separately by God himself just as they are today, but was created to make the study of living beings easier.
Linnaeus and the two kingdoms of life. Painting by Alexander Roslin, 1775.
When the first unicellular organisms were discovered by Antoine van Leeuwenhoek in 1674, they were placed in one of the two kingdoms of living beings, according to their characteristics. It remained so until until 1866, when Ernst Haeckel proposed a third kingdom of life, which he called Protista, and included all unicellular organisms in it.
Haeckel and the three kingdoms. Photo by the Linnean Society, 1908.
Later, the development of optic and electronic microscopy showed important differences in cells, mainly according to the presence or absence of distinct nucleus, leading Édouard Chatton to distinguish organisms in prokaryotes (without a distinct nucleus) and eukaryotes (with a distinct nucleus) in a paper from 1925. Based on it, Copeland proposed a four-kingdom system, moving prokaryotic organisms, bacteria and “blue-green algae”, into the kingdom Monera. The idea of a ranking above kingdom came from this time and so life was separated in two empires or superkingdoms, Prokaryota (Monera) and Eukaryota (Protista, Plantae, Animalia).
Since Haeckel, the position of fungi was not well established, oscillating between kingdoms Protista and Plantae. So, in 1969, Robert Whittaker proposed a fifth kingdom to include them, the called Kingdom Fungi. This five-kingdom system remained constant for some time; Monera were prokaryotes; Plantae were multicellular autotrophs (producers); Animalia multicellular consumers; and Fungi multicellular saprotrophs (decomposers). Protista was like the trash bag, where anything that doesn’t fit in the other 4 kingdoms was placed in.




THE FOUR RIGHTLY GUIDED CALIPHS
http://www.ducksters.com/history/islam/caliphate.php
The First Four Caliphs The Rashidun Caliphate consisted of the First Four Caliphs of the Islamic Empire. Rashidun means "rightly guided." These first four caliphs were called "rightly guided" because they were all companions of the Prophet Muhammad and learned the ways of Islam directly from Muhammad. The Rashidun Caliphate lasted for 30 years from 632 CE to 661 CE. The First Four Caliphs included Abu Bakr, Umar Ibn al-Khattab, Uthman ibn Affan, and Ali ibn Abi Talib.
Read more at: http://www.ducksters.com/history/islam/caliphate.php
This text is Copyright © Ducksters. Do not use without permission.
I POSTED FROM TEXT BOOKS A LONG TIME AGO STUFF ON THE FOUR MUSLIM CALIPHATES AND HOW THE FOURTH THE OTTOMAN WAS DIFFERENT- A THREE PLUS ONE- OTHER CALIPHATES EXISTED BUT THEY ONLY EXISTED SIMULTANEOUSLY TO THE FOUR MAJOR ONES AND ONLY LASTED A COUPLE YEARS IN ATTEMPTS TO TAKE OVER THE FOUR MAJOR CALIPHATES
https://jogajungle.wordpress.com/2013/06/04/caliphate/
During the medieval period, three major caliphates existed: the’ Rashidun’ Caliphate (632–661), the ‘Umayyad’ Caliphate (661–750) and the ‘Abbasid’ Caliphate (750–1258))
(the fourth major caliphate, the ‘Ottoman Caliphate’, established by the ‘Ottoman Empire’ in 1517, was a manifestation whereby the Ottoman rulers claimed ‘caliphal authority’)

THE SMASHING PUMPKINS CROSS
http://www.theraydiantlabyrinth.com/files/1414/0104/3361/scan0007.jpg
http://www.theraydiantlabyrinth.com/index.php/music/sp-cross/
The Smashing Pumpkins' Cross
"Machina" Promotion card on every theatre seat for The Smashing Pumpkins European pre-tour, January 2000

MADONNA CROSS IMAGERY
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Like_a_Prayer_(album)
The music video for "Like a Prayer" was a lightning rod for religious controversy, using Catholic iconography such as stigmata and burning crosses, and a dream about making love to a saint, leading the Vatican to condemn the video and causing Pepsi to cancel Madonna's sponsorship contract. The music video for "Express Yourself" was the most expensive video at its release. Like a Prayer preceded Madonna's ground-breaking Blond Ambition World Tour. At the end of the 1980s, following the release of Like a Prayer, Madonna was named "Artist of the Decade" by several publications.
According to Douglas Kellner, the album and its singles were particularly influential on the music video field.[141] The video for the title track "Like a Prayer", which depicted Madonna as a witness to a murder of a white girl by white supremacists, Catholic symbols such as stigmata, Ku Klux Klan-style cross burning, and a dream about kissing a black saint, was extremely controversial and gained a great deal of attention.
Like a Prayer, alongside Madonna's following album, I'm Breathless, was promoted in her third concert tour, the Blond Ambition World Tour, which visited Asia, North America and Europe. Originally planned as the "Like a Prayer World Tour",[44] it consisted of 57 dates and was divided into five different sections; the first inspired by the 1927 German expressionist film Metropolis, the second by religious themes, the third by the film Dick Tracy and cabaret, the fourth by Art Deco, and the fifth was an encore. The show contained sexual themes and Catholic imagery, such as in the performances of "Like a Prayer" and "Oh Father, which were based in church-like surroundings with Madonna wearing a crucifix and her backup dancers dressed like priests and nuns.


LIKE A PRAYER AND CROSSES- MADONNA WEARING A CRUCIFIX
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Madonna-Like_a_Prayer-Music_Video.jpg
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Like_a_Prayer_(song)
"Like a Prayer" is a song by American singer Madonna, from her fourth studio album of the same name. Sire Records released it as the album's lead single on March 3, 1989. Written and produced by Madonna and Patrick Leonard, the track denoted a more artistic and personal approach to songwriting for Madonna, who believed that she needed to cater more to her adult audience. The song is about a passionate young girl in love with God, who becomes the only male figure in her life.
Madonna in the music video for "Like a Prayer", dancing in front of burning crosses
Madonna lies down on a pew and has a dream in which she is falling through space. Suddenly, a woman, representing power and strength, catches her. She advises Madonna to do what is right and tosses her back up.[61] Still dreaming, Madonna returns to the statue, which transforms into the black man she had seen earlier. He kisses her forehead and leaves the church as she picks up a knife and cuts her hands, bleeding. Interspersing scenes show Madonna singing and dancing wildly in front of burning crosses, erotic scenes between her and the saint, and the singer being surrounded by a choir inside the church.[61] Madonna wakes up, goes to the jail and tells the police that she had witnessed the crime and that the black man is innocent; the police release him. The video ends as Madonna dances in front of the burning crosses, and then everybody involved in the story line takes a bow as curtains come down on the set.[61]
The video received mostly positive response from the journalist and critics. Jamie Portman from The Daily Gazette felt that the clip could be "vulnerable to charges of being blatantly provocative in its calculated blending of sex and religion".[60] David Rosenthal from The Spokesman-Review found the video as "visually stunning";[77] however, Edna Gundersen from USA Today did not understand the media mayhem behind the clip. She pointed out that "Madonna is a good girl in the video. She saves someone. What is the big deal?..."[78] Among music critics, Phil Kloer from Record-Journal felt that whether one condemns the video as racist or not, "It's condemnable on the face of it because it exploits a symbol of evil [the burning crosses of the Ku Klux Klan] in order to sell records."[71] Writing for the Los Angeles Times, Chris Willman complimented the video for its portrayal of a love song, rather than blasphemy. He was more interested in the stigmata presented in the clip.[79] Taraborrelli described his thoughts: "Madonna danced with such abundance in [the video], as if she knew that she was about to cause a commotion, and couldn't wait to see how it would unfold."[80]
The first live performance of "Like a Prayer" was on the 1990 Blond Ambition World Tour. She sang it wearing a dress that looked like a cross between a Mediterranean widow's attire and a clergy's robe. Hundreds of burning candles surrounded her as she knelt down in front of the stage, the backup singers crying the words "Oh my God" several times. Madonna eventually removed a scarf from her head to display a huge crucifix hanging from her neck, and then rose and sang the full song, while her dancers gyrated around her.[93] Two different performances were taped and released on video: the Blond Ambition: Japan Tour 90, taped in Yokohama, Japan, on April 27, 1990,[94] and Blond Ambition World Tour Live, taped in Nice, France, on August 5, 1990.[95] On his review of the latter release, Entertainment Weekly's Ty Burr praised the "gymnastic dance productions in songs such as 'Where's the Party' and 'Like a Prayer'", calling them "astonishing".[96]
PMS DAWN ALBUM STANDING CRUCIFORM AND THE TITLE IS THE CROSS
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Of_the_Heart,_of_the_Soul_and_of_the_Cross:_The_Utopian_Experience
Of the Heart, of the Soul and of the Cross: The Utopian Experience is the debut album by American hip hop group P.M. Dawn. It was recorded at Berwick Street Studios and Gee Street Studios in London.[2] The album features soul vocals and stream-of-consciousness raps by Prince Be and unconventional samples by producer DJ Minutemix.[3]
Of the Heart, of the Soul and of the Cross was released by Gee Street Records in September 1991 to rave reviews from music critics.[4] It became an immediate commercial success with the help of its single "Set Adrift on Memory Bliss", which was also praised by critics.[5] The album produced four hits and sold 850,000 copies by 1993.[6] Of the Heart, of the Soul and of the Cross has sold one million copies.[7]


STARTING AT THE BEGINNING OF THE SONG AT 10 SECONDS THE WOMEN ARE CIRCLING AROUND A CROSS/QUADRANT- THE WHOLE MUSIC VIDOE IS FULL OF CROSS/QUADRANT IMAGERY- PM DAWN SET ADRIFT ON MEMORY BLISS
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0AOVf9p9ht4
Quadrant
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=30RX1yi2V9c
REALITY USED TO BE A FRIEND OF MINE CROSS IMAGERY






THE FOUR MEMBERS OF A TRIBE CALLED QUEST
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/A_Tribe_Called_Quest
Q-Tip
Phife Dawg (deceased)
Ali Shaheed Muhammad
Jarobi White
Q-Tip (Kamaal Ibn John Fareed) and Phife Dawg (Malik Izaak Taylor) were childhood friends who grew up together in Queens, New York. Initially, Q-Tip performed as a solo artist under the name MC Love Child, occasionally teaming up with Ali Shaheed Muhammad as a rapper and DJ duo. While the duo frequently made demos with Phife, then known as Crush Connection, Phife only became a full member once Jarobi White joined. The group's final name was coined in 1988 by the Jungle Brothers, who attended the same high school as Q-Tip and Muhammad.[6] Q-Tip made two separate appearances on the Jungle Brothers' debut album, Straight Out the Jungle, in the songs "Black is Black" and "The Promo".
In early 1989, the group signed a demo deal with Geffen Records and produced a five-song demo, which included later album tracks "Description of a Fool", "I Left My Wallet in El Segundo" and "Pubic Enemy". Geffen decided against offering the group a recording contract, and the group was granted permission to shop for a deal elsewhere. After receiving lucrative offers for multi-album deals from a variety of labels, the group opted for a modest deal offered by Jive Records. Jive Records was then known as an independent rap label that partly owed its success to building the careers of artists Boogie Down Productions and Too Short.
I POSTED ALL THIS STUFF YEARS AGO
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Cross_of_Changes
The Cross of Changes is the second studio album by the German musical project Enigma, headed by Romanian-German musician and producer Michael Cretu, released on 6 December 1993 by Virgin Records internationally and Charisma Records in the United States. Following the unexpected worldwide commercial success of the first Enigma album, MCMXC a.D. (1990), Cretu began to write and record music for a new album at A.R.T. Studios, his home studio in Ibiza, Spain. Cretu samples songs from several artists, including Vangelis and U2.
THE FIRST ENIGMA ALBUM FEATURES A CROSS ON THE COVER
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MCMXC_a.D.
The album's artwork was designed by Johann Zambrysky, who would design the covers for the next four Enigma albums. It depicts a black frame surrounding a silhouette of a figure being enshrouded in a bright light, and a Christian cross in the lower centre of the album for emphasis towards the themes of the album.
Several quotes are printed on the booklet, including the following:
The path of excess leads to the tower of wisdom.
— William Blake (a misquote of "The Road of Excess leads to the Palace of Wisdom.")
The pleasure of satisfying a savage instinct, undomesticated by the ego, is uncomparably much more intense than the one of satisfying a tamed instinct. The reason is becoming the enemy that prevents us from a lot of possibilities of pleasure.
— Sigmund Freud
If you believe in the light, it's because of obscurity, if you believe in happiness it's because of unhappiness, and if you believe in God then you'll have to believe in the devil.
— Father X, Exorcist, Church of Notre Dame, Paris
The cover of the "Limited Edition" of the album is the same as for the original release, but has a grainy dark green background instead of black. The first million copies of the album also have a holograph of the monk and cross on top of the album instead of the normal art work. The sleeve bears a strong resemblance to that of the 1986 Dead Can Dance album Spleen and Ideal.
ENIGMA CROSS COVER
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Enigma_Return_to_Innocence_single_cover.jpg
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Return_to_Innocence
"Return to Innocence" is a song by Romanian-German musical group Enigma. It was released on January 4, 1994 as the lead single from their second album, The Cross of Changes.
JUSTICE ALBUM CROSS
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cross_(Justice_album)
† (pronounced and alternatively known as Cross; considered self-titled on several countries' iTunes Stores[1][2]) is the debut studio album by French electronic music duo Justice. It was first released on 18 June 2007 through Ed Banger Records and Because Music in most countries and Vice Records in the United States.
ALBUM CALLED A CROSS THE UNIVERSE BY JUSTICE- THE T IN JUSTICE ON THE COVER IS A CROSS
A Cross the Universe is the first live album by the French electronic music duo Justice, released on 24 November 2008 on iTunes and on 9 December 2008 physically by Ed Banger Records, Because Music and Atlantic Records. The album's title is a play on words of The Beatles song "Across the Universe" and the band's own album †. The live portion of this release was recorded at a concert in San Francisco, California at the Concourse Exhibition Center, on March 27, 2008. The CD also came with a DVD of the film of the same name called A Cross the Universe.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/A_Cross_the_Universe_(album)
Quadrant
SECOND ALBUM COVER CROSS
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Audio,_Video,_Disco
Audio, Video, Disco. is the second studio album by the French electronic music duo Justice, released on 24 October 2011 by Ed Banger Records, Because Music and Elektra Records.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Woman_(Justice_album)
THE THIRD ALBUM COVER OF JUSTICE IS ALSO A CROSS
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Justice_-_Woman_artwork.jpg
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Woman_(Justice_album)
Woman is the third studio album by the French electronic music duo Justice, released on 18 November 2016 by Ed Banger Records and Because Music.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Justicecross1.jpg
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Justice_(band)
Justice at Fabric with the large illuminated cross they typically perform alongside
JUSTICE CROSS SHIRTS
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Justice_(band)
Justice was nominated for Best Dance Recording (for "D.A.N.C.E.") and Best Electronic/Dance Album (for †) at the 50th Grammy Awards.[18] Justice released their music video for "Stress" on 1 May 2008. The clip features a group of youths committing acts of vandalism and harassment, wearing jackets bearing the Justice cross on the back. Accused in some quarters of racism for its stereotypical depiction of youths of African descent (both black and North African) from Paris' socially deprived banlieues (outer suburbs), others saw the video as a critique of the portrayal of blacks in the French media.[19] Speaking in an interview with The Quietus website, Augé said, "We were expecting some fuss obviously, but definitely not on those topics... If people see racism in the video, it's definitely because they might have a problem with racism; because they only see black people beating up white people, which is not what happens."[20]
De Rosnay said, "Eighty percent of France is Christian." In an interview for Dummy in 2005, Justice said that it wanted a strong concept for each record it put out, and with this one, the duo wanted to keep people guessing.[21]







4 NON BLONDES
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8SbUC-UaAxE
GUNS N ROSES A LOT OF CROSS IMAGERY

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/No_Doubt
No Doubt is an American rock band from Anaheim, California, that formed in 1986. Since 1994, the group has consisted of vocalist Gwen Stefani, bassist and keyboardist Tony Kanal, guitarist and keyboardist Tom Dumont, and drummer Adrian Young.

THE FOUR MEMBERS OF SMASHING PUMPKINS
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Smashing_Pumpkins
The Smashing Pumpkins[1] are an American alternative rock band from Chicago, Illinois, formed in 1988. Formed by frontman Billy Corgan (lead vocals, guitar) and James Iha (guitar), the band included D'arcy Wretzky (bass guitar) and Jimmy Chamberlin (drums) in its original incarnation. It has undergone many line-up changes over the course of its existence, with the current lineup being Corgan and rhythm guitarist Jeff Schroeder.

THE CROSS IN NIRVANA'S HEY WAIT
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heart-Shaped_Box
The video begins and ends with the band in a hospital setting watching an old man being administered medication through an IV drip. The majority of the video takes place in a surreal outdoor setting that incorporates imagery from the film The Wizard of Oz.[22] During the song's first verse, the old man from the hospital climbs onto a crow-ridden Christian cross. The second verse introduces a young girl in a white robe and peaked cap reaching for human fetuses in a tree, and an overweight woman in a suit with human organs painted onto it and with angel wings affixed to her back. In the video's final cut, the band is only shown performing in the outdoor setting during the choruses, where Cobain's face moves in and out of focus in the camera.[22] While most of the video was devised by Cobain, Corbijn added elements such as the intentionally artificial crows, a ladder for the old man to climb onto the cross with, and a box with a heart at the top that the band performs inside of during the song's final chorus.[23] Corbijn created another cut of the video featuring alternate footage during the final verse, including more shots of the young girl and the woman, and scenes of Cobain lying on his back in the poppy field, with mist surrounding him. This version of the video is featured on the DVD The Work of Director Anton Corbijn.[24][25]

THE BIG FOUR THRASH BANDS
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thrash_metal
Four American bands—Anthrax, Megadeth, Metallica, and Slayer—are credited with pioneering and popularizing the genre. The Clash of the Titans tour (1990–1991), which featured Megadeth, Slayer, and Anthrax, is considered the genre's pinnacle, after which thrash metal saw a decline in popularity throughout the decade. Thrash metal has seen a resurgence in recent times, with many of the older bands returning to their roots with their new releases. A new generation of thrash metal bands emerged in the early 2000s, drawing lyrical and visual inspiration from the older groups.
In 1981, a Southern California band Leather Charm wrote a song entitled "Hit the Lights". Leather Charm soon disbanded and the band's primary songwriter, vocalist/rhythm guitarist James Hetfield met drummer Lars Ulrich through a classified advertisement. Together, Hetfield and Ulrich formed Metallica, the first of the "Big Four" thrash bands, with lead guitarist Dave Mustaine, who would later form Megadeth, another of the "Big Four" originators of thrash, and bassist Ron McGovney. Metallica later relocated to the San Francisco Bay Area. McGovney was replaced with Cliff Burton, and Mustaine was later replaced with Kirk Hammett. "Hit the Lights" was featured on their first studio album, Kill 'Em All, released in mid–1983.[12]
The term "thrash metal" was first used in the music press by Kerrang! magazine's journalist Malcolm Dome while making a reference to the Anthrax song "Metal Thrashing Mad".[13] Prior to this, Metallica frontman James Hetfield referred to Metallica's sound as speed metal or power metal.
Another "Big Four" thrash band formed in Southern California in 1981, when guitarists Jeff Hanneman and Kerry King met while auditioning for the same band and subsequently decided to form a band of their own. Hanneman and King recruited vocalist/bassist Tom Araya, a former respiratory therapist, and drummer Dave Lombardo, a pizza delivery driver, and Slayer was formed. Slayer was discovered by Metal Blade Records executive Brian Slagel while performing Iron Maiden's "Phantom of the Opera" at a show, and were promptly signed to the label. In December 1983, less than six months after the release of Kill 'Em All, Slayer put out their debut album, Show No Mercy.
In September 2009, it was announced that Metallica's Lars Ulrich was attempting to assemble a tour with the "Big Four" on one bill. The bands shared the stage for seven shows during the Sonisphere Festival concert series. The first gig took place in Warsaw, Poland, and the last one was in Istanbul, Turkey. In May 2010, Metallica announced that the concert in Sofia, Bulgaria on June 22, 2010 would be transmitted via satellite to movie theaters across the United States, Europe, Canada, and Latin America. The show also provided the historic moment of all current members of the Big Four (with the exception of Slayer members Tom Araya, Kerry King and Jeff Hanneman) sharing the stage to perform the song "Am I Evil?" by Diamond Head.
FOUR MEMBERS METALLICA
METALLICA COVER CROSSES- CROSSES IN THE SKY WHILE FILMING
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Master_of_Puppets
The cover was designed by Metallica and Peter Mensch and painted by Don Brautigam. It depicts a cemetery field of white crosses tethered to strings, manipulated by a pair of hands in a blood-red sky.
The cover was designed by Metallica and Peter Mensch and painted by Don Brautigam. It depicts a cemetery field of white crosses tethered to strings, manipulated by a pair of hands in a blood-red sky. Ulrich explained that the artwork summarized the lyrical content of the album—people being subconsciously manipulated.
While filming its 3D movie Metallica: Through the Never (2013) at the Rogers Arena in Vancouver, crosses were rising from the stage during the song, reminiscent of the album's cover art.[73



