I'm a paragraph. Click here to add your own text and edit me. It's easy.
I'm a paragraph. Click here to add your own text and edit me. It's easy.
http://paei.wikidot.com/o-connell-sean-reason-and-ethics
In Decisions and Dilemmas: A Primer in Ethical Theory, Sean O’Connell introduces principles of reasoning and categories of ethical argument. These are offered as an introduction to philosophy, specifically the subdomains of critical thinking and applied ethics (O’Connell, 1994). Each of these two models reflects the structure of concern. They are described in turn below.
PAEI_085_OConnell_Philosophical_Principles.gif
O’Connell’s introduction to critical thinking presents the following four principles that philosophers are said to use when evaluating arguments (presented in PAEI order):
P – The Principle of Rationality
A – The Principle of Objectivity
E – The Principle of Coherence
I – The Principle of Clarity
P – The Principle of Rationality
Claims must be supported by reasons, and only the best possible reasons. If there is no valid link to evidence that will back the claim, there is no reason to pay attention to it. Scepticism and the immediate rejection of weak arguments are implied.
A – The Principle of Objectivity
The reasoning should be good for everyone. No matter where you are, if you accept the premises, you can repeat the reasoning to arrive at the conclusions without disagreement. The reasoning is acceptable to all parties. The pre-emptive avoidance of dispute is implied.
E – The Principle of Coherence
Claims must be either true or false, not both. If a body of ideas sometimes affirms two incompatible truths (violating the principles of non-contradiction and the excluded middle), then a higher-order argument needs to be constructed to clarify this anomaly and rectify the entire body of thought. Synoptic or higher-order argument structures are implied.
I – The Principle of Clarity
Conclusions and their warrants should always be presented in the clearest possible language, so that consensus regarding their meaning and import can be reached. The mutual orientation of many agents around a common ground of shared representations is implied.
PAEI_086_OConnell_Ethical_Theories.gif
In addition to these principles of informal reasoning, O’Connell further offers a typology of normative ethical theories that also falls along the lines of the structure of concern.
P – Teleological theories
A – Deontological theories
E – Virtue and Character
I – Contractarianism
P – Teleological theories
Acts and rules are defined as right or wrong by virtue of the outcomes they bring about. Includes utilitarianism and other consequentialist theories. It is easy to justify violating a rule or procedure in this framework if the most ethical outcome seems to require it.
A – Deontological theories
Acts are right or wrong to the degree to which they respect or violate moral rules or maxims. Defining the rule properly can be a delicate procedure, but once it has been accepted as right then it is always wrong to violate it. Following the rules becomes everyone’s moral duty, even if the consequences are unpleasant or sub-optimal at times. Following the rule has a value in itself which far compensates for the aversive outcome.
E – Virtue and Character
Virtue theories define ways of being that lead to the most satisfying kinds of human life. Rules, standards and the outcomes of actions are all of minor or conditional interest in the cultivation of a form of being that produces goodness. Unethical behaviours emerge out of vices or defects of the self that cause the agent misery and the desire to remedy them. Perfection of the self is the pathway to goodness, on this view.
I – Contractarianism
Immorality emerges naturally during periods of social disintegration and chaos, in the contractarian view. This is overcome by a collective commitment to compromise individual freedoms and live according to a set of rules that can be enforced. By this means the interests of all are integrated with each other in ethically appropriate ways. Contractarianism finds expression in both economics and political science as well as philosophy, and now supports a very elaborate literature.
At his point it may be worth pointing out that O’Connell’s four ethical categories here map closely onto the four categories of the Ethical Awareness Inventory, put out by the Williams Institute for Ethics and Management (WIEM). This inventory defines four ethical styles, where people judge moral goodness according to: P-Results, A-Obligation, E-Character, I-Equity.
Taken together, O’Connell’s two typologies provide a point of entry for analysing concern structure dynamics within these two sub-domains of philosophy.


http://paei.wikidot.com/birnbaum-bill-strategic-thinking-a-four-piece-puzzle
The Structure of Concern Project compares many theoretical models from many disciplines to the Adizes PAEI model, arguing that they must all be reflecting the same underlying phenomenon. One concern structure model is described below.
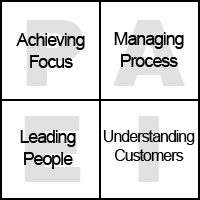
Bill Birnbaum is a strategy consultant with decades of experience helping management teams define their business strategies. In a book called Strategic Thinking: A four-piece puzzle (Birnbaum, 2004), he offers four key components of strategy that follow a concern structure pattern.
P - Achieving and maintaining focus
A - Managing both projects and processes
E - Leading and motivating people
I - Understanding and responding to markets and customers
I POSTED THE STUFF IN THIS BOOK YEARS AGO BUT NOW IM HOPEFULLY ABOUT TO POST IT IN THE SUMMARY SECTION OF THE quadrantmodel.com WEBSITE
http://paei.wikidot.com/bridges-william-transitions
The Structure of Concern Project compares many theoretical models from many disciplines to the Adizes PAEI model, arguing that they must all be reflecting the same underlying phenomenon. One concern structure model is described below.
http://paei.wikidot.com/local--files/bridges-william-transitions/PAEI_010_Bridges_Transitions.gif
William Bridges is a writer, consultant and lecturer in the field of transition management. One of his best known books, dating from fairly early in his career in change management, is called Transitions: Making Sense of Life’s Changes (Bridges, 2004[1]). There he describes a model of transitions that are “on the CUSP of change”. This is the moment where the value of a change is just on the point of being realized, and resistance or hesitation is about to be released. It is the point at which a person becomes open to a change, or willing to engage it. Perceptions switch from more pessimistic to more optimistic ones, as the potential benefits of the change begin to become clear. Personal statements recasting the change as positive emerge, such as – “There is an opportunity to learn here”, “I can gain something important”, “Whatever happens, I’ll come out of this wiser than I went in”.
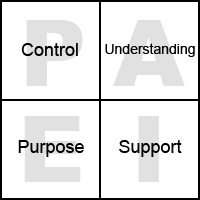
The CUSP acronym represents four factors of change. A person will be successful in managing a personal transition depending on how they feel about these four factors. The factors are listed in CUSP order below, which is PAIE in Adizes terminology. Reorganizing CUSP into PAEI order would result in the less helpful acronym CUPS.
P – Control: Do you feel you have control of the situation?
A – Understanding: Do you truly comprehend what is happening and why?
I – Support: Do you have (or can you obtain) the practical and emotional support for what you are going through?
E – Purpose: Do you have a sense of purpose to give meaning and direction to your experiences and actions?
It thus takes the activation of the full structure of concern to orient oneself to major changes in one's circumstances.
I DESCIRBED TO YOU ALL I LISTENED TO AUDIOBOOKS SINCE 2009 WHEN I DISCOVERED THE QUADRANT MODEL FROM EVERY SUBJECT I WOULD GO TO THE LIBRARY AND JUST SKIM THROUGH BOOKS DOMINANTLY ALL THAT WAS TAUGHT WAS THE QUADRANT MODEL
http://paei.wikidot.com/brill-worth-four-levers-of-corporate-change
Complex management problems need to be tackled from more than one angle. Managers need many different tools or points of leverage to get things to happen in organizations. In The Four Levers of Corporate Change (Brill & Worth, 1997[1]), Brill and Worth identify four different ways in which managers can actually effect real change in organizations.
http://paei.wikidot.com/brill-worth-four-levers-of-corporate-change
P – Skillful use of Power
A – Well-designed Social Processes
E – Persuasive Leadership
I – Understanding of Human Nature
P – Skillful use of Power
Managers faced with trenchant opposition to change can simply act. They can use their position to make pre-emptive organizational changes that alter the composition of their opposition. Managers can use their authority to restructure a team in ways that will destabilize deadlocked groups. They can also monopolize communication channels to promulgate a vision. They can use diplomacy and bargaining to sway individuals towards their cause, and they can control how change efforts are announced, launched and scheduled, etc. The power wielder can make these moves, hoping that at some point the opposition will fade and their changes will become self-perpetuating. The direct-action aspect of this mode puts it in the P domain of concern.
A – Well-designed Social Processes
Rather than immediately engaging conflict head-on, change can sometimes be aided by designing a social process to achieve the end in mind. This requires an understanding of human nature and a strategic mind. Suppose a group of subordinates feel that their supervisors are poor at delegating. Rather than just telling the supervisors, you can ask them to participate in a process of self-assessment, rating how they think their subordinates feel about their own delegation skills. These scores can then be compared with subordinates ratings of their managers, and the discrepancy pointed out. The issue then becomes one of the inaccuracy of managers’ self-images, instead of an accusation from the floor. The well-designed process applies all of the pressure for change without anybody having to take an offensive or defensive stand. The structure communicates the message, putting this in the A mode.
E – Persuasive Leadership
Leaders must inspire by example, and assemble a cadre of other inspired leaders within the organization, all of whom can be persuaded to back the same mission. This kind of leadership requires vision and self-knowledge. Good leaders recognize other informal leaders in the group and put them in strategic organizational positions. Leaders must maintain an overall sense of mission and yet be able to pay full unbiased attention to the particulars of any problem brought to their attention. They must resolve problems according to their particulars, but always in a direction that supports the mission. They must also manage alliances, including upwards, downwards and horizontal relationships between their organization and others. Persuasive leadership requires vertical flexibility and the capacity to deploy long-term and short-term thinking as needed. The strategic overview required for this strategy is situated in the E domain.
I – Understanding of Human Nature
The human factor can make or break any change effort. Leaders have to gather info about peoples’ feelings and beliefs, not accepting all statements at face value. Strong empathy skills are required, as well as an appreciation for the quirks and paradoxes of the human mind and heart. Leaders have to be wise in their use of reward and sanction, which means they have to know what motivates different people. This lever underlies the other three, and is… pivotal for their success. The focus on the human element puts this in the I domain.

http://paei.wikidot.com/duke-corporate-education-stakeholder-styles
The Structure of Concern Project compares many theoretical models from many disciplines to the Adizes PAEI model, arguing that they must all be reflecting the same underlying phenomenon. One concern structure model is described below.
In a book called Influencing and Collaborating for Results, the writers at Duke Corporate Education (2005) introduce a four-part typology of stakeholder personality styles, positioning it as a kind of summary of various personality measures that managers might have encountered in their careers. The four personality types are:
P – Skeptic: Risk-averse and not willing to rock the boat. Follows the “if it ain’t broke, don’t fix it” approach. Doesn’t consider all new ideas as “advances”.
A – Evaluator: Cautious, but willing to take calculated risks if the facts support it. Will want to see the supporting data and give careful analysis.
E – Enthusiast: Open to new ideas and trying new approaches. Enthusiastic, optimistic, a “big picture” visionary or entrepreneur. Likely to look for and take advantage of new opportunities that are tightly connected to strategy.
I – Angler: Less concerned about the project itself and more concerned about the political implications and personal benefits of involvement. Interested in what he or she can gain by engaging in the challenge. Looks for all the angles.

The Structure of Concern Project compares many theoretical models from many disciplines to the Adizes PAEI model, arguing that they must all be reflecting the same underlying phenomenon. One concern structure model is described below.
http://paei.wikidot.com/fahey-narayanan-macroenvironmental-analysis
In their textbook on Macroenvironmental Analysis for Strategic Management (Fahey & Narayanan, 1986[1]), Fahey and Narayanan describe dimensions of the business environment that are relevant for the construction of business strategy. These dimensions are also relevant to the structure of concern. Fahey and Narayanan indicate that managers need to undertake analyses of the environment of their organizations in order to understand current and potential business changes. They can also use these analyses to generate important intelligence for strategic decision makers. Fahey and Narayanan review several business environment models, and draw a distinction between models of the general environment and those of the business-relevant environment. They divide the business-relevant environment into four segments, along the lines of the structure of concern:
P – Economic: Gross measures of productive activity at local, regional and national levels, and relationships to demand.
A – Political: The regulatory environment, but control over regulatory bodies is contested, so PI-type political processes and developments are highly relevant.
E – Technological: Progress, advancements, innovations and discoveries are the key concerns in the technological sector.
I – Social: Demographics, lifestyles and cultural values all matter in this sector, and can be related to demand, productivity and political processes.
Their model of macroenvironmental analysis highlights the linkages within and between these segments. Environmental turbulence is analyzed as changes in interconnectedness within and among segments.

16 TYPES 16 SQUARES QUADRANT MODEL
http://paei.wikidot.com/garrison-b-r-plus-32-employment-testing-system
The Plus-32 Employment Testing System is an employee profiling software package based loosely upon the Hippocratic/Galenic temperament model. It sorts personality factors into four main groups. All people have all four personality factors, but only to a certain percentage value for each group. There are 16 personality types, based on the different possible rankings of the four groups. A 17th type "E" is added, indicating someone who is equal in all four main categories. Thus, unlike Adizes or Jungian type theories, it is possible (though thought rare) for someone to be equally strong in all areas (Garrison, 1998[1]).
The Plus 32 system contains pattern-detection algorithms that try to filter out the effects of equivocation between test items, or of employees parroting buzzwords that are known to be important to the corporate culture, but which do not reflect their actual personality. A Plus 32 report thus includes a consistency rating, indicating how consistent a subject's answers were according to the categories of the system. Less confidence is accorded to less consistent results.
The system has been validated by exit interviews among test groups. Profiles for different job functions in an organization are developed through local benchmarking. Human resource officers divide the employees within a job category into thirds, and look for profile similarities and differences among the top-third performers, middle-third performers and lower-third performers. The results of this benchmarking indicate that different profiles characterize top performers doing the same job in different companies, reflecting different corporate cultures and local market situations.
This instrument measures 18 personality traits (listed below) to determine the role of each of the following four personality types in each person.
Type A: The Leader
Type B: Have Personality Will Travel
Type C: The Serious One
Type D: Happy Go Lucky
The order of these four types in Adizes terminology is PEAI.
P - Type A; The Leader: Motivated by money and challenge. Tend to lead, not follow. No patience for fuzzy thoughts or actions that do not lead directly to tangible results or a monetary reward. They hate soft-skills seminars. They only want to hear about the bottom line. They do not take direction well, and have little compassion. To direct them, you have to ask them what they think should be done, debate pros and cons with them, and show them how your proposed direction benefits them more than any alternative.
E -Type B; Have Personality Will Travel: A talker, a people-person who demands recognition and attention, and a constantly changing work environment. They tend to get bored easily. They require direction and thrive on hype and excitement. They hate details, facts and figures, and have short attention spans. They want to try everything without finishing anything. They are flexible and will handle shifts in task assignment well. They have huge egos, and are best rewarded by recognition. They appreciate praise and pep-talks. Although they are very competitive for honors, money means little to them.
A - Type C; The Serious One: Prefer things to be uniform/consistent, professional and reliable. They enjoy technical posts involving detailed charts and graphs. Thrives on routine, perfection, detail and analysis. There is no room for hype in their world. They work on a task until it is completed, by the book. Do not pull them off a half-finished task to work on another one. They need a regular environment, same desk, same hours, clear rules and boundaries, etc. They are loyal in stable situations. They are anchors, rather than movers and shakers.
I - Type D; Happy Go Lucky: Do better in low-key positions. Have pleasant personalities and get along with most people. Do well in customer service, or areas where stability and balance are needed. They have little need for hype or change. They are patient, they like teamwork, and they work at their own pace, neither fast nor slow. They are not hugely ambitious, and they prefer not to rock the boat.


THE FOUR MEMBERS OF STONE TEMPLE PILOTS ARE A THREE PLUS ONE WITH THE FOURTH DIFFERENT THREE CONSISTENT
Current members
-
Dean DeLeo – guitar (1989–2002, 2008–present)
-
Robert DeLeo – bass, backing vocals (1989–2002, 2008–present)
-
Eric Kretz – drums (1989–2002, 2008–present)
-
Jeff Gutt – lead vocals (2017–present) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V5UOC0C0x8Q
No. 4 (officially stylized as № 4) is the fourth album released by American hard rock band Stone Temple Pilots, released on October 26, 1999, by Atlantic Records.

Venni Vetti Vecci is the debut studio album by American hip hop recording artist Ja Rule.
JA RULE'S ALBUM COVER HAS CRUCIFORM CHRIST- JA RULE IS SHORT FOR THE TETRAGRAMMATON RULE- JA RULE WAS RAISED A J WITNESS
The Last Temptation is the fourth studio album by Ja Rule.
HE HAS CROSS TATTOOS ON HIS BACK AND CROSSES ON THE ALBUM COVER


https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Abbey_Road
Abbey Road is the eleventh studio album by English rock band the Beatles, released on 26 September 1969 by Apple Records.
The album's cover features the four band members walking across a zebra crossing outside Abbey Road Studios and has become one of the most famous and imitated images in the history of popular music.

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Abbey_Road_E.P.
The Abbey Road E.P. is an EP by The Red Hot Chili Peppers, released in the UK in May 1988 through EMI America as a way of introducing UK fans to the band's back catalog as they were touring the UK that year.
The title and cover was a tribute to The Beatles' famous album Abbey Road. Like the Beatles, the cover depicts the four bandmembers walking across a zebra crossing in single file, the twist being that they are all naked except for white tube socks covering their genitals. Wearing only socks in this manner was something they regularly employed in their stage shows at the time. All songs on the EP were also featured on the band's hits compilation, What Hits!?.[3]

http://knowyourmeme.com/photos/276209-abbey-road-parodies
http://knowyourmeme.com/memes/abbey-road-parodies
Parodies of Abbey Road predate the Internet in popular culture. One of the earliest known parodies of the album was the release of McLenore Avenue by Booker T. & The M.G.’s in April 1970, featuring the members walking across the street outside Stax Studio in Memphis, Tennessee.[3] The album payed tribute to the Beatles, consisting of instrumental covers of Abbey Road.

The Geto Boys is a remix album by the Geto Boys released in 1990. The cover of the album resembles The Beatles' album Let It Be, and the songs attracted much controversy upon the album’s release.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Geto_Boys_(album)
THE FOURTH GETTO BOY IS DIFFERENT AND WAS NOT IN SOME OF THE ALBUMS
-
DJ Ready Red

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mind_Playing_Tricks_on_Me
In his album The B. Coming, Beanie Sigel, in the highly acclaimed song "Feel it in the Air", recycles a lyric from Scarface's intro to the song - "I sit alone in my four cornered room".
Let It Be is the twelfth and final studio album by the English rock band the Beatles.


Hot Space is the tenth studio album by the British rock band Queen.

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Demon_Days
Demon Days is the second studio album by British virtual band Gorillaz, released on 11 May 2005 in Japan and on 23 May internationally by Parlophone Records and in the United States by Virgin Records.

Van Halen is the debut studio album by American hard rock band Van Halen. Released on February 10, 1978, the album peaked at number 19 on the Billboard 200.

Labcabincalifornia is the second album by The Pharcyde, released in 1995, three years after their debut Bizarre Ride II the Pharcyde.
There Is Only Now is the sixth studio album by American hip hop group Souls of Mischief.

https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0VwfYCFYZws
THE FOUR MEMBERS OF SOULS OF MISCHIEF

Monkees
"Listen to the Band:25th Anniversary"
THE ROLLING STONES OFTEN HAD 5 MEMBERS BUT ON SOME ALBUMS THEY HAD FOUR- FIFTH IS ULTRA TRANSCEDENT QUESTIONABLE FOURTH IS TRANSCENDENT- QUADRANT ALBUM COVER PARODY BEATLES LET IT BE
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Emotional_Rescue
Emotional Rescue is the 15th British and 17th American studio album by The Rolling Stones, released in 1980. Upon release, it topped the charts in both the US and UK.

Remain in Light is the fourth studio album by American new wave band Talking Heads, released on October 8, 1980 through Sire Records. It was recorded at Compass Point Studios in the Bahamas and Sigma Sound Studios in Philadelphia between July and August 1980 and was produced by the quartet's long-time collaborator Brian Eno.

https://reptiliandimension.files.wordpress.com/2015/03/denverrunway2.jpg
To the right is a aerial picture of Denver airport. Notice that the runways and airport are built in the shape of a Nazi swastika.


U2
"Pop"
http://www.amiright.com/album-covers/images/album-U2-Pop.jpg
http://www.amiright.com/album-covers/beatles-let-it-be-parodies/
Apparently inspired by Queen's cover for "Hot Space" whcih was inspired by The Beatles' "Let it Be" - so it does count as a parody/inspiration/spoof - Submitted by: Lee

THE U2 ALBUM COVER IS A 16 SQUARE QUADRANT MODEL FOUR MEN CUTTING DOWN A TREE
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Achtung_Baby
The band referred to the album's musical departure as "the sound of four men chopping down The Joshua Tree".
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HOWAyBbN3C0
U2 AND SONG THE TETRAGRAMMATON
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Yahweh_(song)
"Yahweh" is a song by rock band U2 and the eleventh track on their 2004 album How to Dismantle an Atomic Bomb. It was mainly recorded in one take, and was performed live by the band during the Vertigo Tour. The song received mixed reviews from critics.
"Yahweh" (יהוה) is the name of the Judeo-Christian God in both the Bible. The oldest Hebrew manuscripts present the name in the form of four consonants, commonly called the Tetragrammaton (from Greek te·tra-, meaning "four", and gram′ma, "letter"). These four letters (written from right to left) are יהוה, transliterated into English as YHWH or JHVH. "Jehovah" is the best known English pronunciation of the divine name, although "Yahweh" is favored by most Hebrew scholars. Some Jews avoid pronouncing the name "Yahweh".

http://www.amiright.com/album-covers/images/album_--10.jpg
http://www.amiright.com/album-covers/beatles-let-it-be-parodies/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Slaughterhouse_(group)
Slaughterhouse is a hip hop supergroup consisting of rappers Joe Budden, Joell Ortiz, Kxng Crooked and Royce da 5'9". They are currently signed to Shady Records under Interscope. They have released two studio albums as a group, the independently released Slaughterhouse and Shady Records backed, Welcome to: Our House.


